OEM Unlock: What it is, Benefits & How to Enable?
Are you having trouble unlocking your OEM? OEM Unlocking is a process that allows users to modify the bootloader of their Android phones. However, it can be challenging to understand why OEM Unlock is necessary and how to enable it.
In this blog, we will cover everything there is to know about OEM Unlock, including its benefits, why manufacturers lock it in the first place, and how to enable it without a password. We will also address common questions such as whether OEM Unlock is the same as rooting, if it wipes data, and how to disable it on your device.
So get ready to become an expert in OEM Unlocking with these tips and tricks!
What is OEM Unlock?

Android smartphones come full of features and capabilities. However, to prevent users from accidentally altering default applications and settings, Android manufacturers conceal certain settings from users. To do so, you need to unlock OEM, also known as Original Equipment Manufacturer. OEM Unlock refers to the process of unlocking your Android phone’s bootloader, which allows you to make modifications to the device’s software. Manufacturers lock the OEM to prevent users from making unauthorized changes that could potentially harm the device or compromise its security.
OEM unlocking in Android extends the usability of the device beyond its initial limitations. It’s important to note, though, that unlocking the OEM on Android will void the warranty. The OEM unlock feature empowers users to unlock all settings and functions on their Android phones, unleashing the device’s full potential. Enabling OEM unlock grants access to customization options and currently restricted features.
Enabling OEM Unlock can be beneficial for those who want to install custom ROMs, gain root access, or perform other advanced customization on their smartphones. However, it is important to note that enabling OEM Unlock will void your device’s warranty and may introduce certain risks.
Why do They Lock OEM?
Manufacturers lock the OEM on Android devices for various reasons. Firstly, it ensures that users do not accidentally modify or delete critical system files that are necessary for the proper functioning of the device. By locking the OEM, manufacturers can maintain a level of control over how their devices are used.
Locking the OEM also helps prevent unauthorized modifications that could potentially compromise the security of the device. Manufacturers want to ensure that users do not install malicious software or make changes that could lead to vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, locking the OEM allows manufacturers to maintain consistency across their devices, ensuring a standard user experience for all users. It also helps manufacturers control the distribution of software updates and ensure that only authorized and tested updates are installed on their devices.
While OEM locking may seem restrictive to some users, it serves a purpose in maintaining the stability, security, and reliability of Android devices. Manufacturers aim to strike a balance between user customization and device integrity, providing users with a safe and reliable experience.
Before deciding to unlock the OEM on your Android device, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks involved. As mentioned earlier, enabling OEM unlock will void your warranty, meaning that any issues or damages caused by custom modifications will not be covered by the manufacturer. This can be a significant concern for users who rely on their warranty for device repairs or replacements.
In addition to warranty concerns, unlocking the OEM carries certain risks that users should be aware of. One of the main risks is the potential for bricking your device. If you make any mistakes during the unlocking process or install incompatible software, it could render your device inoperable.
Another risk is the increased vulnerability to security threats. Unlocking the OEM allows for the installation of custom ROMs and mods, which may not have undergone the same level of security testing as official software releases. This increased vulnerability can expose your device to potential malware or other security risks.
OEM Unlock Benefits
Enabling OEM unlock on Android devices comes with several notable benefits, which can enhance your overall user experience and expand the capabilities of your device. Here are the primary advantages:
- Unlocking Bootloader: By enabling OEM unlock, you gain the ability to unlock your device’s bootloader. This is essential for advanced customization and installing custom software.
- Installing Custom Recovery: OEM unlock allows you to replace the stock recovery with a custom recovery, such as TWRP recovery mode. Custom recoveries offer more advanced options for backup, restore, and flashing custom ROMs.
- Installing Custom ROMs: With an unlocked OEM, you can easily install custom ROMs, which are alternative operating systems for your Android device. Custom ROMs often provide improved performance, unique features, and the latest Android updates for older devices.
- Rooting Device: Enabling OEM unlock is a prerequisite for rooting your device. Rooting provides administrative access, allowing you to remove restrictions, customize your device deeply, and run apps that require root access.
- Installing Custom Kernel: Custom kernels can enhance your device’s performance and battery life. OEM unlock enables you to install custom kernels tailored to your specific needs.
- Removing Bloatware: Bloatware or pre-installed apps that cannot be uninstalled can be removed or disabled after OEM unlock. This frees up storage space and can improve device performance.
- Installing Mods: OEM unlock permits the installation of mods that can customize default buttons for various actions, enabling you to tailor your device’s functionality to your preferences.
- Accessing and Modifying System Files and Partitions: You gain the ability to access and modify system files and partitions, providing advanced users with greater control over the inner workings of their Android devices.
Disadvantage of OEM Unlocking on Android
In addition to the benefits, there are certain drawbacks associated with unlocking OEM on Android devices. The primary disadvantage is that unlocking the OEM will immediately void your warranty. Additionally, there are other potential drawbacks to consider:
- No More Software Updates: After unlocking OEM, your Android device may no longer receive official software updates from the manufacturer. This can leave your device running on older software versions, potentially missing out on new features, security patches, and performance enhancements.
- Increased Vulnerability: Unlocking OEM can make your Android device more vulnerable to hackers, attackers, and spyware. Without the manufacturer’s security safeguards, your device may become more susceptible to security threats.
- Risk of Bricking: Improperly unlocking the bootloader can lead to a situation where your Android device becomes unusable, commonly referred to as “bricking.” This is a significant risk if the unlocking process is not followed correctly.
- Potential for System File Issues: If you’re not familiar with the process or mishandle custom ROM installations, you may inadvertently disable or remove important system files, making your device unstable or non-functional. OEM unlocking can expose these critical files to potential harm.
Why would you need to enable OEM Unlocking?
There are a few key reasons why someone may want to enable OEM unlocking on their Android device:
For one, unlocking the bootloader allows you to install custom firmware, kernels, and operating systems. With an unlocked bootloader, you are no longer limited to the software provided by the device manufacturer. You can install custom ROMs like LineageOS to get new features, customization options, and potentially better performance or battery life. For Android enthusiasts and power users, the ability to flash custom ROMs is a major benefit.
Additionally, an unlocked bootloader is required to gain full root access on a device. Root access allows modifying system-level files and settings for advanced customizations. With root, you can install mods, run specialized apps, automate tasks, customize the UI, and more. Many apps and capabilities require a rooted device.
Developers may also need an unlocked bootloader for debugging and development purposes. It gives access to the system partition for testing apps and modifications. The ability to flash unsigned code and make changes is critical for development work.
There are some risks, like potential for bricking the device, voiding the warranty, and decreased security. But for many Android users, the benefits of an unlocked bootloader outweigh the risks. It opens up a whole new level of customization and control over your device’s software.
Why Is OEM Unlock Missing?
There are a few common reasons why the OEM unlock option may be missing from your Android device settings:
- The device manufacturer has chosen to permanently disable the OEM unlock option. Some OEMs like Xiaomi and Motorola completely remove the unlock ability on many models to increase security.
- The carrier has requested the removal of OEM unlock for devices sold specifically by that carrier. Carriers sometimes enforce this to prevent customers from tinkering with devices on their network.
- The device is a carrier-branded model. Carrier versions often come with restrictions including the inability to unlock the bootloader. Only unlocked models directly from the OEM will have OEM unlock.
- The device does not meet certain requirements imposed by the OEM. For example, Samsung OEM only allows unlocking after a waiting period from device purchase date, and only on certain hardware variants.
- The device has been refurbished or relocked by the OEM/carrier after being returned. Refurbished units often have OEM unlock disabled.
- The device’s bootloader is already unlocked, so the unlock option disappears. An unlocked bootloader cannot be re-locked on most devices.
- The device is running older Android firmware that did not include an OEM unlock toggle in settings. The feature was added in later versions.
How to Enable OEM Unlock without Password [Free download tools]
Unfortunately there is no way to enable OEM unlock on most modern Android devices without the device password. Here are the reasons why:
- The OEM unlock setting is kept in the encrypted settings storage on the device. This requires password authentication to access.
- Even if you factory reset the device, Android requires you to enter the previous primary account’s password after reset to prevent unauthorized access.
- For older devices with unlock codes, a factory reset won’t reset the unlock code. You still need it to enable OEM unlock.
- Hidden developer menus that allowed backdoor unlock access have mostly been removed by OEMs due to security reasons.
- Modifying the lock state on system partitions to bypass the password is not feasible for most users and would void your warranty.
- Temporary bootloader unlock methods using engineering bootloaders have been patched by OEMs.
- Unofficial modified firmware that allows unlocking is hard to obtain, alters your system, and voids the warranty.
- Hardware methods like booting specialized unlock tools require dismantling the device which is risky.
Overall, there are no official tools to do so. However, If you still want to try doing it, there are some after market tools like iMobie, FoneDog, iToolab, iDelock etc that claim to do so. These tools are available as a free download and may help you do and bypass FRP information and Google account verification.
Perform Samsung OEM Unlock Without Code Needed
Unlocking the Samsung OEM status on your device can be a tricky process, but it’s crucial to remember your credentials to avoid being locked out. However, if you find yourself locked out due to forgotten passcodes or other issues, there’s hope in the form of FoneDog Broken Data Extraction software. This powerful tool can recover data from various Android device problems, including forgotten passwords, broken screens, system crashes, and more. The blog post outlines a step-by-step guide on how to effectively use FoneDog to recover your valuable data.
How to Enable OEM Unlock on Your Samsung Device
If you own a Samsung device running Android 5.0 Lollipop or a later version, you might have noticed that the OEM unlock option is missing from the developer options. Samsung has removed this option as a means to access the bootloader on their devices. However, there’s still a way to enable OEM unlock if you wish to do so.
Here’s how you can achieve this:
- Obtain a tool called Odin. Odin is a software program designed for flashing firmware and other files onto your Samsung device. You can find the latest version of Odin available for download on various websites.
- Once you’ve downloaded and installed Odin, launch the program on your computer and connect your Samsung device to it using a USB cable.
- After your device is connected, locate and click on either the “PDA” or “AP” button within the Odin interface.
- Choose the file named “CODE_SAMSUNG-RECOVERY.tar.” This specific file is what enables the OEM unlocking feature on your device.
- Now, click on the “Start” button in Odin and wait for the process to complete. Your device will undergo a reboot as part of this process.
- Once the process is finished, your device will restart, and you will now have the ability to unlock the bootloader using the standard method, which involves using the command “fastboot oem unlock.”
Enabling OEM unlock allows users to unlock the bootloader of their device, giving them more control over their Android system. However, this process can have consequences such as tripping Knox, Samsung’s security feature. Once you enable OEM unlock and install a custom ROM on your Samsung device, the Knox security feature will be disabled, which may leave your device vulnerable to security threats. It’s important to note that unlocking the bootloader can also void the warranty and disable certain features like Samsung Pay.
How to Enable OEM Unlocking on Android?
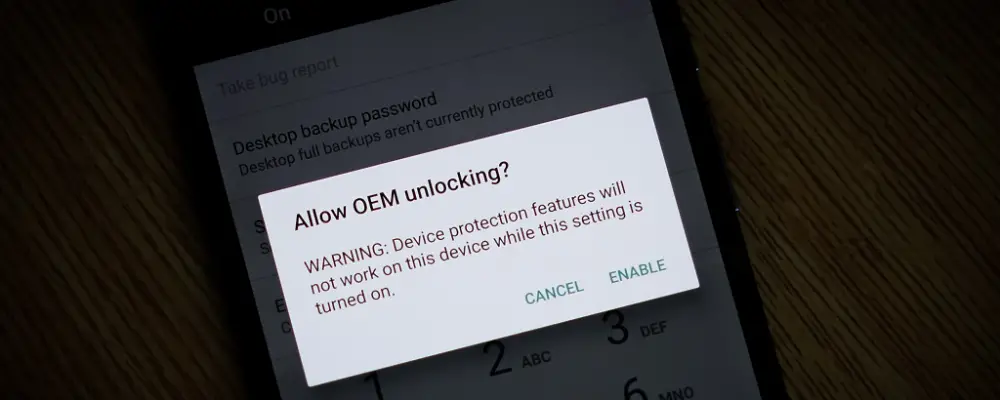
OEM unlocking empowers your device to install the Android bootloader and custom ROMs, unlocking its full potential.
Here are the steps to enable OEM unlocking:
Step 1:Enable Developer options
To activate developer options on your Android device, follow these steps:
- Access your device’s “Settings.”
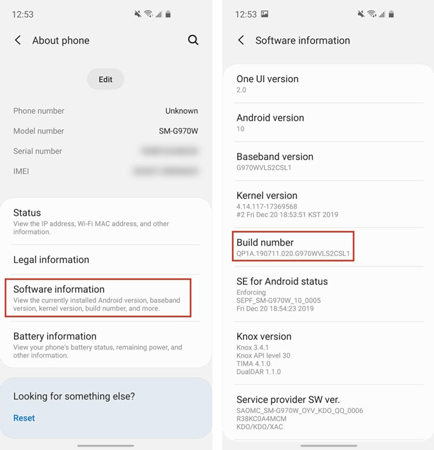
- Navigate to “About Phone.”
- Tap on the “Build Number” option seven times. You’ll receive a confirmation pop-up that says, “You are now a developer,” indicating that developer options have been successfully enabled.
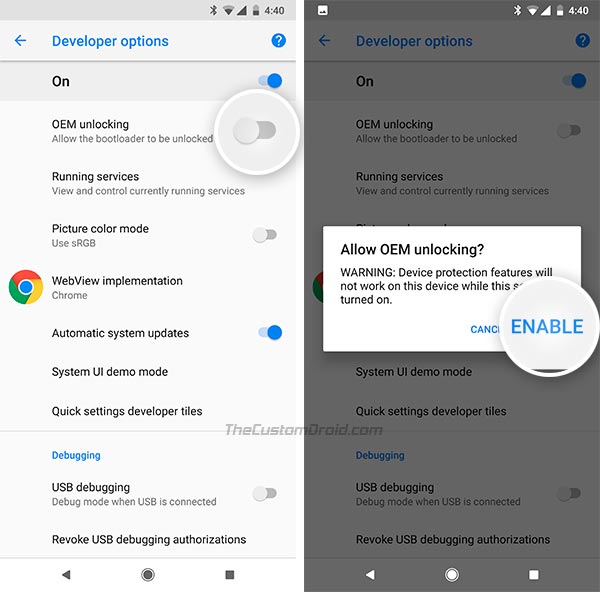
Step 2:Enable OEM unlock From developer option
Here are the steps to enable OEM unlocking on your Android device:
- Open “Settings.”
- Locate and tap on “Developer options.”
- Find and select “OEM unlocking.”
- On the “Allow OEM Unlocking Warning” screen, tap “Enable.”
This will activate OEM unlocking on your Android device, allowing you to use ADB for activities like rooting, installing custom ROMs, or adjusting settings.
Please note that the menus in the Settings app may vary between different Android devices. To enable developer options, remember to find the “Build Number” option in your device’s settings and tap it seven times. Additionally, the location of developer options may differ; in Android Nougat and newer versions, it’s typically found under “Settings” > “System.”
Enabling OEM Unlock vs. Unlocking Bootloader
There is an important distinction between enabling OEM unlock and actually unlocking the bootloader on an Android device:
- Enabling OEM unlock simply allows you to unlock the bootloader – it does not unlock it directly. You still have to issue the fastboot oem unlock command to unlock the bootloader.
- The OEM unlock toggle is found in the Developer options section of your device settings. Toggling it on just enables the ability to unlock the bootloader.
- Unlocking the bootloader requires connecting the powered off device to a computer and issuing fastboot commands. The actual unlock command erases user data.
- After enabling OEM unlock, rebooting the device does not wipe data. The bootloader remains locked. Data is only erased when you send the unique unlock command.
- OEM unlock can be re-disabled later without affecting the bootloader lock state. But unlocking the bootloader cannot be reversed on most devices.
- Unlocking the bootloader will show a warning screen on future device boots that the bootloader is unlocked. OEM unlock alone does not trigger this.
What is a Bootloader on Android?

A bootloader is a crucial piece of software responsible for initializing the device’s boot-up sequence and creating a bridge between the device’s hardware and software.
When you power on your device, the bootloader takes center stage, loading the operating system from storage into memory. This process enables the device to gain access to its hardware components, including input/output functions and storage.
How to Fix No OEM Unlock in Developer Options
No matter why you’re facing the issue of “OEM Unlock missing,” there are various methods you can attempt to recover this option. It’s important to note that certain phone models, such as Snapdragon-powered phones in North America, may have restrictions on unlocking the bootloader. However, you can still give it a try, as Samsung’s policies may change in the future, potentially allowing more users to unlock the bootloader.
Method 1: Fix OEM Unlock Missing by Changing the Date
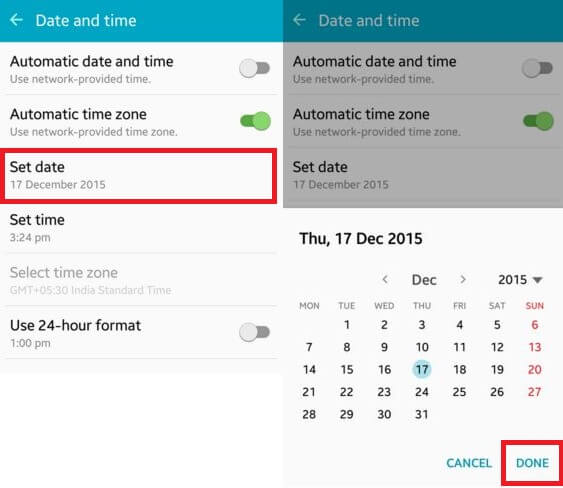
If the OEM unlock option is missing from your device’s developer options, you can try this method, especially if your device is new. Follow these steps:
- Open the Settings on your Galaxy phone.
- Navigate to “General Management” > “Date and Time.”
- In the Date and Time section, turn off “Automatic date and time.”
- Set the date manually to a date from the last month or earlier.
- Return to the main Settings menu and then go to “About Phone” > “Software Information.”
- Tap the “Build number” option seven times to enable developer options.
- Now open the developer options on your phone.
- Look for the “Auto Update System” option and disable it.
- Next, go to “Settings” > “Software Update” and disable the “Auto download over Wi-Fi” option. You can now check for updates manually, and you can ignore any error messages if they appear.
- Once done, reboot your device.
- Go back to the developer options, and you should now find the “OEM Unlocking” option.
This method provides an easy way to address the issue of the missing OEM unlock option in developer options. If it doesn’t work for you, we can explore other methods.
Method 2: Fix No OEM Unlock by removing the SIM

If the first method didn’t work, you can modify it slightly and try again. Here’s what you can do:
- Remove the SIM card from your phone and prepare for a phone reset, as enabling OEM unlocking will reset your device anyway.
- Reboot your phone and connect it to Wi-Fi to start the setup process.
- During the setup, skip the login for both your Gmail and Samsung accounts. If this step doesn’t work initially, try logging into both accounts and then proceed.
- Follow all the steps outlined in method 1.
- Check the Developer Options, and you should now find the “OEM Unlocking” option available.
This adjusted approach may help you successfully enable OEM unlocking if the initial method did not work.
Method 3: Fix the OEM Unlock Missing by flashing the Firmware
Occasionally, resolving the issue of “OEM Unlock missing” from the developer options involves flashing the firmware, either the same version or from a different region. However, it’s important to note that mistakes in the flashing process can lead to a bootloop, so it’s crucial to be prepared to recover from this situation.
Here’s how you can attempt this method:
- Download the firmware you want to flash, preferably from the same region as your device. You can use tools like Frija or Samsung Firmware Downloader for this purpose.
- Obtain the Odin Tool, which is used to flash the firmware. Ensure that you select CSC (Consumer Software Customization) and not the CSC Home option. Detailed steps for this process can be found here.
Taking these steps with caution can help you address the issue of “OEM Unlock missing” in the developer options by flashing the firmware. However, please be aware of the potential risks and ensure you are familiar with the recovery process for a bootloop situation.
How to Disable OEM Unlock on Android?
If you wish to deactivate OEM Unlock, you can follow these steps, which are similar to the ones mentioned above:
- Launch the Settings app either from the App Drawer or the Notification/Control Center.
- Navigate to the System Settings.
- Scroll down to find Developer Options.
- Locate the OEM Unlock option and toggle the switch to the left to disable it.
FAQ’s:
Does Enabling OEM unlock void the warranty of the device?
No, enabling OEM unlocking does not void the warranty on your Android device. However, installing a custom ROM or unlocking the bootloader may lead to warranty voidance.
Is OEM unlock the same as root?
No, OEM unlock and rooting are distinct processes. Rooting provides you with full control and administrative access over your device, whereas OEM unlock solely pertains to unlocking the bootloader. While unlocking the bootloader is a prerequisite for rooting, they are not synonymous actions.
Can I Root Andriod Without unlocking the bootloader?
Yes, you can root your Android without unlocking the bootloader. Rooting and unlocking the bootloader are two separate things. But, the simplest way to root a device is by unlocking the bootloader.
Does OEM unlock wipe data?
Yes, the OEM unlock process on Samsung Galaxy devices can potentially result in data loss or corruption, particularly if you have a carrier-locked device.
Carrier-locked devices often disable the OEM unlock toggle as a precautionary measure. Unlocking the bootloader, which is a part of the OEM unlock process, can involve erasing or resetting the device, potentially causing data loss.
Therefore, carriers often restrict this option to safeguard user data and maintain control over device configurations. If you intend to unlock the bootloader and enable OEM unlock, it’s crucial to back up your data to prevent any unwanted data loss during the process.
My OEM Unlock Options turned grey?
Many Galaxy smartphones sold in the USA and Canada have Snapdragon chipsets, and these often come with bootloaders that cannot be unlocked. As a result, you may notice that the OEM unlocking option is either greyed out or not available at all.
Is OEM unlocking safe?
Enabling OEM unlocking itself is safe, as it’s an official feature provided by Android manufacturers. However, the actions you take after unlocking the bootloader, such as installing custom software or making system modifications, can introduce security risks, potentially void your warranty, and may require technical expertise.
Conclusion
To sum it up, enabling OEM unlock can provide you with greater flexibility and control over your device. It allows you to customize your device, install custom ROMs, and unlock its full potential. However, it’s important to remember that enabling OEM unlock may void your device’s warranty and can carry certain risks.
Make sure to fully understand the implications and follow the necessary steps carefully. If you encounter any issues or have questions, refer to the FAQ section for more information. Take advantage of the benefits that OEM unlock offers, but proceed with caution and make informed decisions to ensure a positive experience with your device.



